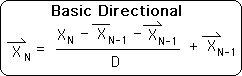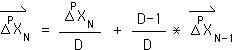Glossary A>F: definitions, descriptions and links of the diverse variety of terms employed throughout the multiple articles devoted to Information Dynamics.
The Active Pulse
The Active Pulse is the name for the Pulse when it occurs in the Triple Pulse. It is first and last pulse of this alternation of pulses. The graph below is a visualization of the Triple Pulse, which contains both the Active Pulse and the Rest Pulse.
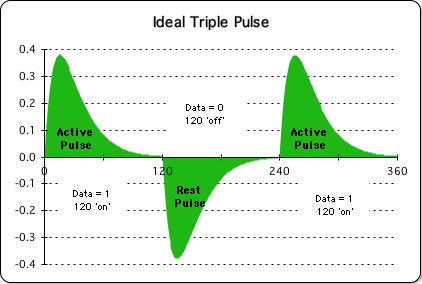
The Triple Pulse is a result when the Living Algorithm digests a specific type of data stream. The standard sequence consists of an uninterrupted string of 120 ones, followed by an uninterrupted string of 120 zeros, followed by another string of 120 ones. The number string of 1s is associated with the Active Pulses, while the number string of zeros is associated with the Rest Pulse.
The Living Algorithm’s computational process reveals the rates of change (derivatives) of a data stream. The Triple Pulse is a visualization of the Living Algorithm's 2nd derivative – the Directional. According to Lehman’s Theory of Attention, the Active Pulse is the mathematical model associated with both the Creative Pulse and the Pulse of Attention. Experimentation combined with analysis has associated the Active Pulse with a creative session, consciousness, and the momentum of attention.
algorithm
"In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list for calculating a function. … In simple words, an algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for calculations. … Giving a formal definition of algorithm, corresponding to the intuitive notion, remains a challenging problem." (Wikipedia)
Some common examples of simple algorithms are the 'step-by-step procedures' that we learn in elementary school to add, subtract, multiply, and divide large numbers. The Living Algorithm of Information Dynamics only employs these simple arithmetic processes. The name 'Living Algorithm' is based upon the 'intuitive notion' of algorithm being a 'step-by-step procedure' for determining an answer.
Molecular & Subatomic Realms
According to the Interacting Realms Paradigm of Lehman's Attention Theory, these are two of the three mathematically based Realms of Existence along with the Non-Material Realm. The Molecular Realm is our traditional material world – reality. It consists of the interaction of particles, e.g. atoms and molecules. Atoms are the building blocks of this realm of existence. Traditional Newtonian Mechanics reveals the laws that govern the Molecular Realm.
The Subatomic World is the micro world of potentiality that exists inside atoms. It consists of subatomic entities, e.g. electrons and photons. Quantum Mechanics reveals the laws that govern the Subatomic Realm.
The interaction between the Molecular Realm and the Subatomic Realm generates the Material Realm. The interaction between the Material Realm and the Non-Material Realm generates the Living Realm.
Molecular Realm x Subatomic Realm = Material Realm
Material Realm x Non-Material Realm = Living Realm
For a more in-depth discussion of these topics, read the article: Attention & Matter: Interacting Realms of Existence?
Attention
According to Lehman's Attention Theory, Attention is a theoretical primitive. As such, it is an essentially indefinable notion. Every logical system contains these theoretical primitives. 'Set' of mathematical set theory is another theoretical primitive, i.e. indefinable. As such, we must appeal to intuition and suggestion to determine the meaning of attention.
Generally speaking, most of us sense that attention is the ability of living systems to focus awareness upon incoming information, whether external or internal, sensory or ideational. Attention corresponds with this notion in our theory. Rather than continuously, information comes in the form of data streams.
For humans, Attention turns 'on' when we are conscious, i.e. awake, and turns 'off' when we are unconscious, i.e. asleep. According to our theory, when Attention is 'on', we take in and digest the information contained in incoming data streams via the Living Algorithm. Conversely, when Attention is 'off', we cease taking in information in order to finish the digestion process.
Due to its association with the Living Algorithm's digestion process, Attention has some special features. For instance, Sustained Attention over a distinct duration is required to have an Experience. This property is due to Attention's linkage to the Pulse, one of the innate mathematical forms of the Living Algorithm. According to the theory, an Experience is an essential requirement for the assimilation and integration of information. Living systems employ this knowledge to fulfill potentials including survival.
For more, check out the treatise: Attention, Life & the Living Algorithm.
Attention Complex
There is a nearly universal consensus amongst the scientific community that all living systems from the single cell to the most complex multi-cellular organisms, e.g. humans, exhibit awareness of their environment, both internal and external. Another name for awareness is the capacity for Attention. Attention exists as a gestalt, i.e. fully separable, yet completely integrated components. As a group, we shall these interconnected capabilities the Attention Complex.
On the most basic level, Attention implies a sense of Being, a Doer, Intention, Feelings, an Executive Function, and Choice.
Rather than free-floating, Attention is instead attached to a living entity (Being), whether a single cell or a human. Being entails a sense of existing as a singular unit (a sense of self is not implied; this comes much later). Being employs Attention as a tool, as an interface with the environment. Attention provides Being with environmental Information. Being employs the Information to make decisions (Choice) about what actions to take (Doing) in order to facilitate survival or to fulfill potentials.
Being must have some kind of innate urges (Feelings) that drive the Intention to survive or fulfill potentials. An Executive Function employs the Information derived from Attention to make choices that will maximize the chances of fulfilling potentials.
There is also a scientific consensus that Attention provides Being with digested, rather than raw, Data. Just as our digestion system transforms raw materials into a form that Body can use for nourishment, Attention transforms raw data streams into a form that Mind can use to make decisions. Our sensory organs, e.g. eyes, are certainly part of the digestion process,
We suggest that there is also a mathematical component to the digestion process. According to Lehman’s Theory of Attention, Attention employs the Living Algorithm (LA) as a computational interface with environmental data streams. The LA provides many useful analytics, e.g. the Predictive Cloud . The LA’s mathematical forms also provide the limitations, which in turn give rise to increasing complexity.
This connection between Attention and the LA has many implications. The LA generates a mathematical system deemed Data Stream Dynamics (DSD). Just as the tides entrain to the gravitational rhythms of the Sun and Moon, living behavior seems to entrain to the mathematical processes of DSD.
In terms of Attention Theory, the Attention Complex also includes the LA as a computational tool. In support of this hypothesis, there are many patterns of correspondence between DSD and an abundance of empirical data.
Attention Formula

The Formula for Attention, at right, encapsulates a basic premise of Information Dynamics theory in a single equation. In brief, the Attention Formula is a mathematical process that exhibits the requirements for how inert Information is transformed into useable Knowledge in living systems. The equation makes many testable predictions. Common experience and experimentation have validated many of these predictions. (For a partial list, check out the glossary entry – patterns of correspondence.)
Let us verbalize the formula. When Attention (circle A) is sustained upon Information (I) for a sufficient duration, it generates an Experience (circle E), whereby the Information is transformed into Knowledge (K), i.e. a change in the neural networks. The Directional's information digestion algorithm (§) drives this entire process.
Each element in the equation has a tightly defined mathematical equivalent. The symbol '§' represents the computational process. '§' is the Directional operator. The Directional is an equation that generates a data stream's directed acceleration at each moment. In the case of the Attention Formula, the Directional only operates upon data streams consisting of identical elements and with a specified length, i.e. Pulse Strings. The Directional Process is repeated enough times to generate a Pulse of Acceleration from these Pulse Strings.
'I' represents the content, i.e. the Information contained in the Pulse Strings. 'Circle A' represents a Pulse of Sustained Attention, i.e. a Pulse String of 1s. 'K' represents the Information once it has been transferred to the neural networks via the Directional's information digestion process. 'Circle E' represents a Pulse of Acceleration.
In the Attention Formula, the Directional operates on a one or more Pulse Strings and generates an equivalent number of Pulse Types. In other words, the answers to the Attention Formula and its derivatives are processes. A data stream of numbers represents these processes. In contrast, the summation operator '∑' adds up a specified string of numbers to yield a single numerical result.
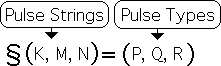
For a more complete discussion of the elements, the context, and the testable predictions of the Attention Formula, check out the article Mathematics of Attention.
Attention Realm
A mathematically based realm of existence that is exclusive to living systems. According to the Interacting Realms Paradigm, Living Behavior is determined by the interaction between the Material Realm and Realm of Attention, i.e. Life’s non-material component.
As opposed to exclusively material systems, all living systems have the capacity for Attention to a greater or lesser degree. Attention belongs to a complex that includes Intention, Feeling, Choice, Information and Mental Energy.
The Attention Realm qualifies as mathematically based realm of existence because Data Stream Dynamics reveals the rules that govern Attention. This mathematical system is based in Reflexive Equations. In contrast, Regular Equations reveal the laws of the Material Realm. The mathematics of both realms, material and non-material, employs traditional Newtonian constructs such as Force.
The Attention Realm is also known as the Non-Material Realm, the Realm of Choice, the Realm of Intention, the Information Realm and the Imaginary Realm, depending upon which feature is being emphasized.
For a more in-depth discussion of these topics, read the article: Attention & Matter: Interacting Realms of Existence?
Attention Pulse (a.k.a. The Pulse )
The Pulse
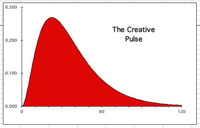
The ideal Pulse is a result when the Living Algorithm digests a data stream consisting of a sufficient number of consecutive 1s (120 in the graph at the right). In the Creative Pulse Notebook, the Author develops the notion that the intriguing curve to the right represents the momentum at each moment in the data stream. In this sense, it could be said that the Pulse represents the momentum of a data stream that contains 120 consecutive '1's. As the momentum of the uninterrupted data stream of 1s grows, the pulse rises to its maximum peak. As the data stream's momentum falls, the curve gradually diminishes, and then ultimately zeros out. Because of the simplicity of the data stream, just 1s, the Author refers to the Pulse as the Living Algorithm's primary mathematical form, i.e. energy pattern.
This model was originally chosen to represent an uninterrupted creative session. Due to the many patterns of correspondence between the Pulse and a productive session, the original name of this flowing curve was the Creative Pulse. It was much later that he realized that this name was both misleading and limiting. Instead of only applying to creative sessions, this mathematical model seems to apply to a broad and significant range of human experience. And instead of being related only to creativity, the mathematical pulse seemed to be related to a natural attention span. It was further supposed that this natural attention span, when uninterrupted, laid the foundation for a productive and creative session. In other words, the mathematical curve shown above seemed to be more related to attention and less related to creativity. With this realization, the name was changed from the Creative Pulse to the Pulse of Attention.
For a more detailed exploration of this significant curve, check out The Pulse of Attention, an Introduction, The Pulse of Attention, the Graph, and The Pulse of Attention Interrupted.
behavioral dynamics
Behavioral Dynamics, Information Dynamics, and Attention Dynamics: These are all names that I have used to refer to the complex of ideas associated with my Theory of Attention. I have employed the same word 'dynamics' in each case because Data Stream Dynamics provides the mathematical foundation for my theory. Attention theory addresses the mathematical relationship between human behavior, Information, and Attention, which is the reason for the qualifying words.
See the glossary entries under Theory of Attention and Data Stream Dynamics for a more up-to-date understanding of Behavioral Dynamics.
Cell Equation, a.k.a. Living Algorithm
The Cell Equation, also called the Decaying Average, has been renamed the Living Algorithm. Check out this glossary item for the meaning of the phrase. We changed the name because the process has nothing to do with biological cells. Further, it is a general algorithm, rather than a specific equation.
Living Algorithm family (formerly Cell Equation family)
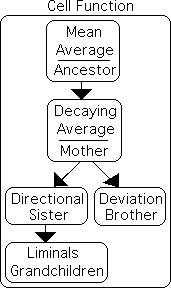
The Living Algorithm, a.k.a. the Cell Function, digests any data stream. The digestive process produces the rates of change (the derivatives) that describe the data stream's ongoing moments. To facilitate understanding we characterize these data stream derivatives as a family of ongoing averages (central measures). The traditional mean average is the ancestor (the Living Algorithm without decay). The data stream's 1st derivative, i.e. the Decaying Average, is the mother. In this role, she gives birth to 2 children, a son and a daughter. These are the data stream's 2nd derivatives. The brother in the family is the Deviation, a sheer magnitude without direction. The sister is the Directional, a directed magnitude. The Directional, in turn, gives birth to the Liminals, the grandchildren of the family. These are the data stream's higher derivatives. Their relationships are shown at right. Check out the article Living Algorithm Family for more information.
The mother (the Decaying Average) indicates the probable location of the next point in the data stream. The son (the Deviation) indicates the range of variation of this prediction, while the daughter (the Directional) reveals the recent tendencies of the data stream. As a group, they are called the Predictive Cloud. Because of their descriptive and predictive capabilities, the Predictive Cloud is very useful to living systems.
Living Algorithm's Unique Graph Design (formerly Cell Equation's …)
Interpreting graphs of this nature requires a special footnote. The values in this particular set of graphs represent a different way of thinking about what are traditionally known as the x and y-axis. The values on the horizontal x-axis represent the number of iterations (repetitions) in the digestive process of the Living Algorithm. As such, the x-axis consists of whole numbers only. Dividing iterations into fractions would be nonsensical. With each iteration of the Living Algorithm process, a new reading is taken and plotted on the graph. The dimensions of the vertical y-axis reflect the values contained in the data stream.
This set of graphs is also unique due to the Living Algorithm's innate nature. The Living Algorithm is not a regular equation, but is instead a recursive function, i.e. iterative and self-referential. There are 3 elements of the Living Algorithm process that characterize the non-traditional nature of these graphs. Initially we note that the substance of the digestive process is unique in that it consists of an ongoing data stream. The process of the Living Algorithm is also unique in that it is both iterative and self-referential. It is iterative in that it is a repetitive process – with each iteration, a sample of the ongoing data stream is taken. This process becomes self-referential because it relates the present sampling to previously digested data.
Living Algorithm System (formerly Cell Equation System)
A mathematical system based in the Living Algorithm's method of digesting data streams.
Significant Features of Data Stream Dynamics (the Living Algorithm System
The Living Algorithm is a recursive function – an iterative equation that refers to itself. In other words, the Living Algorithm's digestive process is self-referencing and is repeated over and over again. Each repetition (iteration) of the process produces the rates of change, i.e. the derivatives, of the current instant/data byte. Just as Material Dynamics
This is a moment. If the information contained in these moments is consistent over a long enough duration, it generates an experience. Mathematically, this is a pulse of momentum. We have deemed this the Pulse of Attention because the mental energy of sustained Attention is required to transform moments into a life-changing experience. These are all features of the Living Algorithm System.
Predictive Cloud provides future estimates that could be useful to Life,
The Predictive Cloud is a particularly significant feature of this mathematical system. These are the cloud of derivatives (rates of change) that surround each data point - the moment. This feature is of particular significance because the Living Algorithm's Predictive Cloud provides data stream descriptors that provide future estimates. This feature is extremely useful to living systems on a moment-to-moment level. As such it provides an evolutionary advantage. For a more in depth coverage of these topics, check out the Living Algorithm System and Evolutionary Potentials.
Living Algorithm provides essential forms for complexity's emergence.
These articles are part of a larger Notebook, Mathematics of Living Systems. The primary purpose of this article stream is to establish that living systems could employ the Living Algorithm to digest sensory data streams. In the crucial role as Life's operating system, the Living Algorithm's innate structures also provide the necessary boundaries that determine what forms that biological systems could take – a grammar of Life. In this role, the Living Algorithm didn't just provide a requisite talent, but actually provides the limits that are essential for the growth of complexity in living systems.
Information Digestion Model
The Living Algorithm System is pure mathematics. The Information Digestion Model is a conceptual model that was developed to make sense of the synergy between the Living Algorithm System and empirical data/scientific 'facts'.
conscious, unconscious, subconscious
These words have simple meanings in the context of Information Dynamics. When an organism is conscious, it takes in information. When an organism is unconscious, it does not take in information. The organism's subconscious processes digest and organize information. This process can happen or not during both the state of consciousness and unconsciousness. Unconscious cognition is the word that cognitive science employs instead of subconscious processes.
Core Postulates
The many correspondences between the mathematics of Information Dynamics and the empirical reality of living systems 'forced' us to make some bold assumptions. These assumptions are radically different from the underlying assumptions of behavioral reality that are currently in vogue. A prevalent scientific mindset is that the mental world is almost totally subservient to the physical world. Indeed some, if not most scientists might say that Mind is a subset of Body with no real autonomy whatsoever. Accompanying this mindset is the notion that choice is but an illusion. It is exciting to present a powerful explanatory theory that is based upon the alternate assumption that Mind and Body are equal players and that Mind has the ability to choose a course of action.
Following are several prime assumptions (core postulates) underlying Info Dynamics theory.
1. Living systems consist of both a material and information-based component (Body & Mind?).
2. These components are autonomous yet interacting systems. They suggest the notion of intersecting orthogonal planes.
3. Living systems digest information via the Living Algorithm.
4. By revealing the dynamics of the moment, the information digestion process relates transforms data streams, environmental and otherwise, into meaningful knowledge that enables the living organism to fulfill potentials.
5. The mathematical method of information digestion also shapes and limits human behavior.
(Check out the article Core Postulates for a more detailed analysis of why we were forced to make these assumptions.)
Creative Pulse
The Creative Pulse, the original name of the Pulse of Attention, is a result when the Living Algorithm digests a data stream consisting solely of 1s. In the Creative Pulse Notebook the Author develops the notion that the intriguing curve to the right represents the momentum at each moment in the data stream. In this sense, it could be said that the Creative Pulse represents the momentum of a data stream that contains 120 consecutive '1's. As the momentum of the uninterrupted data stream of 1s grows, the pulse rises to its maximum peak. As the data stream's momentum falls, the curve gradually diminishes, and then ultimately zeros out.
The Author performed a computer experiment on this ideal Creative Pulse. He sensed, from his own experience, that interruptions to his creative sessions seemed to have a disproportionate negative impact. He deems this the Interruption Phenomenon. As it was based upon a data stream consisting of an uninterrupted series of 120 1’s, the Creative Pulse model was chosen to represent an uninterrupted creative session - hence its name. To simulate interruptions to a creative session, the Author altered the ideal data stream by introducing interruptions in the form of 0s at a variety of locations along the stream. He called this series of manipulations the Creative Pulse Experiment. It turns out that this mathematical model reveals that interruptions to the data stream do have a disproportionate, negative effect upon the ideal dimensions of the Creative Pulse. The findings of these experiments are located in the Creative Pulse Notebook and reviewed in the article Pulse of Attention Interrupted. The excellent fit between mathematics and experience inspired him to further explore the model. The Triple Pulse Experiments were one result of this exploration.
Other articles concerning the Creative Pulse include: Applications and Elements.
Living Algorithm program (formerly Creative Pulse program)
An Excel spreadsheet that employs the Living Algorithm to compute the derivatives of any data stream. This program also generates the all-important graphs for Information Dynamics.
data digestion vs. data processing
Rather than the more traditional word 'process', I employ the word 'digest' to indicate the Living Algorithm's computational process. The reasons are twofold. First, Infodynamics theory links food digestion with the LA's data digestion process. One provides nourishment for the Body; the other for the Mind. A secondary intent is to differentiate the LA's computations from standard electronic processing. While electronic processing frequently aims at exact replication, whether text, music or video, the LA's digestion process generates composite figures. Although incorporated into these composite measures, the raw data is lost.
data set & data stream
A Data Set consists of a static number of clearly defined data points. Data Sets are the substance of the mathematics of Probability. Probability utilizes fixed and invariable central measures, such as mean average and standard deviation, to characterize data sets.
In contrast, a Data Stream is a growing set of ordered Data points. This distinguishes it from a Data Set, with its static set of Data points. In order to process a data stream, Probability must treat it as a fixed Data Set. The Living Algorithm treats the data stream, not as a fixed set, but as a living set. It does so by computing the ongoing derivatives of any information flow.
For a more thorough discussion check out the Data Stream Momentum Notebook.
Data Stream Dynamics
A mathematical system that was specifically designed to characterize the dynamics of data streams. Based upon the Living Algorithm's computational process, DSD was inspired by the constructs of Newtonian dynamics, e.g. acceleration, force and inertia. Indeed, data stream dynamics and material dynamics share a nearly identical architecture, i.e. underlying inferential structure. These ideas are developed in the Notebook – Data Stream Dynamics.
While they share the same architecture, the two mathematical systems apply to entirely different realms. Newtonian dynamics is the basis of Material Mathematics, while we hypothesize that Data Stream Dynamics (DSD) is the basis of the Mathematics of Attention. For instance, Newtonian dynamics reveals many of the laws that govern material behavior, while DSD seems to provide at least some of the rules that govern living behavior, specifically those associated with Attention.
Lehman's Theory of Attention is based in part upon the mathematical forms generated by Data Stream Dynamics. These forms appear to provide at least some of the limitations that enable the development of complexity in living systems. As an example, just as Matter, both animate and inanimate, entrains to the rhythms of the Sun and the Moon, the rhythms of Attention seem to entrain to the rhythms of Data Stream Dynamics.
data stream momentum
Data stream momentum is a mathematical method for determining the momentum of a flow of information and the attendant inertia to changes in that data stream. In other words, the method examines the pattern of energy in a series of moments as a way of analyzing the strength of a habit. As such, it is a way of quantifying the energy or strength of habits.
Data Stream Momentum is also the name of an entire notebook devoted to the mathematical development of the concept. Because of the presumed importance of this notion, a collection of notebooks from the Author's creative obsession of 1994 was given this same title.
Decay Factor
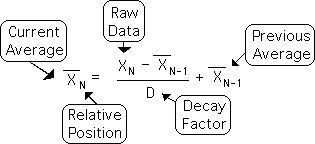
The Decay Factor is a highly significant feature of the Living Algorithm. The most basic form of the algorithm, the Decaying Average, is shown at right. As the name indicates, D, the Decay Factor, determines the rate of decay in the equation. They are inversely related. The higher the Decay Factor, the slower the rate of decay; and vice versa.
Although D can be any positive value, we can divide the Decay Factor’s continuum into 5 pragmatic sectors:
instantaneous (D=1)
volatile (D=2 through 9)
stable (D=10 through 20)
sedentary (D=20 through 50)
eternal (D greater than 50).
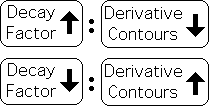
The Decay Factor article illustrates the effects of different ranges of D upon a single data stream. In brief, the Living Algorithm’s Decay Factor is inversely related to the shapeliness of the contours of the Data Stream Derivatives. Decay Factor up; Contours down. And vice versa. (Note: When the Decay Factor is set at 1, the instantaneous range, there are no rates of change, hence no data stream derivatives.)
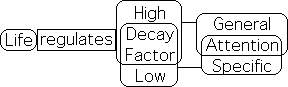
If living systems employ the Living Algorithm to digest information, they could also have evolved to take advantage of the Decay Factor's talents. If so, then living systems could regulate the Decay Factor to shift between specific and general attention, the two phases of the well-established Posner Attention Model. We further suggest that general attention is the default mode and that it requires mental energy to move the Decay Factor down into the specific attention range. The default mode could be a way of conserving mental energy for other endeavors.

In the article on the Sleepiness Phenomenon, we argue that it even takes mental energy to maintain the high Decay Factor that is required for general attention. As this mental energy is depleted, the Decay Factor begins rising into the eternal range. The environmental contours become flat and we eventually go to sleep. Sleepiness is a sign that our mental energy is insufficient to regulate the Decay Factor any longer.
Decaying Average (a.k.a. Living Average)

The Decaying Average is the 1st derivative of a data stream, as computed by the Living Algorithm. It is similar to a 'running average'. As such, it is not a single point, but a data stream.
The equation is shown at right. It utilizes the Xs with subscripts (XN) and bars (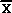 ) to identify the Decaying Average. Subscripts indicate the Decaying Average's place in the data stream and the bar indicates that it is an average rather than an individual data point.
) to identify the Decaying Average. Subscripts indicate the Decaying Average's place in the data stream and the bar indicates that it is an average rather than an individual data point.
The algorithm for computing the Decaying Average is a simple procedure.
- 1) Determine the difference between the most recent data point and the previous Decaying Average.
- 2) Scale this difference proportionately.
- 3) Add or subtract the scaled difference to the previous Decaying Average. (Add if the data point is larger than the previous Decaying Average. Subtract if the data point is smaller than the Decaying Average.)
- 4) The result of this process is the new Decaying Average.
This simple procedure turns the existing Decaying Average into the previous Decaying Average and, in so doing, produces the next Decaying Average in the data stream. This process continues with the input of each new data point, relegating each Decaying Average into a proportional part of the past Decaying Average. Check out the Decaying Average Notebook for more details, including basic applications and fundamental rationale.
A few more points of note:
When the Living Algorithm is applied to the Decaying Average data stream, it produces the second derivatives of the original data stream. One is a sheer magnitude, a scalar, while the other is a directed magnitude, a vector. Like the Decaying Average, these are also data streams.
Deviation is the name of the scalar derivative, as it indicates the ongoing range of the original data stream. Directional is the name of the vector derivative, as it indicates the ongoing tendencies of the original data stream. As a group, these three most basic data stream derivatives, including the Decaying Average, are called the Predictive Cloud.
The reason for the name is straightforward. The trio of measures provides immediate descriptors of any data stream that can be employed to predict the probable location of the next point in the stream. We argue elsewhere that if living systems were to employ these ongoing predictive measures, it would provide a crucial evolutionary advantage.
The Decaying Average and the traditional Mean Average, while sharing some similarities, have some distinct differences. Both are averages and even have a similar equation. A single Mean Average characterizes a data set, no matter how large it is. This number describes the entire data set. In contrast, it takes a data stream of Decaying Averages to characterize a data stream. This averaging of the ongoing flow of information weights the most recent data points more heavily, while proportionately diminishing the weight of past data points. As such, it best describes individual moments, not in the entire data stream. As such, the Decaying Average is applicable to the data stream's context, while the Mean Average is applicable to the data set's context.
derivatives
On the most fundamental level, a derivative is a rate of change. It is called a derivative because it derives from some kind of change that occurs over time. This time can be real or mathematical, in the sense that it is an abstraction. Derivatives also change over time. As such, it is possible to also compute a higher-level derivative to characterize this rate of change. For example, a car's acceleration, the 2nd derivative, is the rate of change of the car's velocity, the 1st derivative. Because this process can be extended indefinitely, there are an infinite number of derivatives.
The Living Algorithm’s sole function is to produce the rates of change/derivatives of a data stream. However, these derivatives are not like the traditional derivatives of calculus. A basic difference is that data stream derivatives are discretized, i.e. broken into discrete parts, while the derivatives of calculus are continuous. As such, data stream derivatives do not require the mathe-magic of calculus, but instead only require common sense arithmetic. Second, data stream derivatives are not meant to model the changes/dynamics of material systems, but are instead meant to model the changes/dynamics of information digestion in living systems. In brief, the derivatives produced by calculus specialize in Matter, while the Living Algorithm’s derivatives specialize in living matter, i.e. Life.
Traditionally, 'derivative' is the mathematical term for an instantaneous rate of change. Calculus is a complicated mathematical process designed to compute derivatives, these instantaneous rates of change. By taking an infinite sum of these infinitely small derivatives, mathematicians regularly come up with something. This mathe-magical process is at the heart of calculus and could be why the word 'derivative' is intimidating to those with a non-mathematical mind.
For a more in depth discussion of this topic, check out the article – Data Stream Derivatives.
Deviation
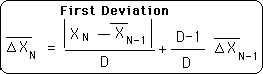
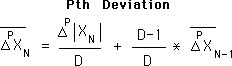
A measure of the undirected acceleration of a data stream. Because it is undirected, the Deviation is a scalar.
The Living Algorithm's information digestion process produces the ongoing rates of change/derivatives for each moment in a data stream. The Deviation, along with the Decaying Average and the Directional are the most significant of these derivatives. As a group, they are called the Predictive Cloud, for the following reason.
According to Information Dynamics theory, living systems could employ these measures to make rough predictions regarding probable location, the range of variation and recent tendencies. It seems that knowledge of these predictive descriptors would maximize the effectiveness of response to environmental stimuli. A more effective response would in turn enhance the possibility of survival, thereby conferring an evolutionary advantage.
If this line of reasoning is correct, living organisms employ the Deviation to determine the ongoing range of variation of a data stream. According to the Boredom Principle, when the Deviation/range of variation shrinks past a threshold, humans begin to experience mental agitation - i.e. boredom. This inner agitation motivates humans to change behavior, perhaps try something new. As such, human boredom is at the root of experimentation, exploration, fashion and art, at least according to Info-Dynamics theory.
Directional
A measure of the directed acceleration of a data stream. Because it is directed the Directional could be considered a vector.
The Living Algorithm's information digestion process produces the ongoing rates of change/derivatives for each moment in a data stream. The Decaying Average is the data stream's 1st derivative (the velocity). The Basic Directional is the 2nd derivative (hence acceleration) of the data stream.
The Creative Pulse, a.k.a. the Pulse of Attention, is a graphic representation of the Directional of a data stream consisting of 120 ones. The Triple Pulse is a picture of the Directional of another binary data stream consisting of 120 ones, 120 zeros, and 120 ones. There is an abundance of evidence, both experiential and experimental, linking these mathematical forms with living behavior.
For more on the mathematics of the Directionals, check out the series of Notebooks entitled Directionals: Content, Context & Beauty. For more on the patterns of correspondence between the Directional and human behavior check out the Notebook entitled the Triple Pulse of Attention.
discovery
In the context of this paper the word 'discovery' means something new to oneself, as in the 'discovery' of a new restaurant, a new hiking spot, or ‘discovering’ something new about oneself.
disobedient/obedient equations
What does it mean for an equation to be disobedient? To understand disobedience, we must first understand what it is to be an obedient, well-behaved, well-founded equation.
A significant branch of Science, some might even claim the main branch, has to do with the application of mathematical symbols to empirical reality. Included in this branch are all the hard sciences, computer science, and most of the soft sciences. This aspect of the scientific endeavor has been based, almost exclusively, upon obedient equations. Only in the last forty years, has the scientific community begun to even consider disobedient equations as a way of describing reality. This shift of focus was due, at least in part, to Mandelbrot’s development of fractal geometry combined with the computer revolution of the late 1970s. Up until that time, any scientific endeavor that had mathematics associated with it was devoted to obedient equations. Even now, obedient equations still have the center stage.
What does it mean for an equation to be obedient?
An obedient equation belongs to the set of well-founded functions in the mathematical lingo. For our purposes, a well-founded function obeys the axiom of regularity. Briefly, this means that the function doesn’t contain itself. In other words, if a function contains itself, it violates the axiom of regularity and is booted from the club of well-behaved functions.
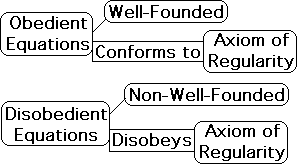
What is it about self-containment that is so repellent to the scientific community that they have ignored this class of equations? Equations that contain themselves don't conform to the laws that govern standard equations. In other words, traditional set theory doesn't apply to them. While there is only type of obedient equation, there are countless types of disobedient equations. Each type of disobedient equation has its own rules. This individuality makes it difficult, if not impossible, to generalize.
More importantly, disobedient equations are not as predictable as obedient equations. For instance, the sophisticated mathematical techniques that scientists have developed to make approximations don't apply to disobedient equations. While generally unpredictable, disobedient equations do yield precise results to specific conditions.
The Living Algorithm of Data Stream Dynamics is a disobedient equation. For a more in-depth discussion of this topic, check out the article: Matter’s Regular Equations vs. Life’s Disobedient Equations.
Doctor Flow
We're applying this apropos nickname to Dr. Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi. This esteemed man spent his entire career investigating the human phenomenon that he deemed Flow - even writing a national bestseller of the same name. Flow is an important process that humans must participate in to have those 'optimal experiences' that make life worth living. Other researchers have shown that these optimal experiences are part of a complex process called 'intrinsic motivation'. According to the theory, this is a basic need that must be fulfilled for a human to be happy, productive, and motivated. The Flow process is related to, if not the same as, the Pulse. Although we know the doctor's name is pronounced 'chick-sent-me-high', this is impossible to discern from the letters, which are even more difficult to spell. Hence the accessible and descriptive nickname.
dumb kid syndrome
In a scientific experiment, students were first asked to evaluate their writing skills. They then graded each others papers. In the final stage of the experiment, they evaluated their skills again. In general, grading the papers helped correct everyone's self-perception. For instance: although the smart kids initially undervalued their skills, they raised their self-evaluation after grading the papers of others. However, a subset of the dumb kids continued to over-value their skills despite being shown papers of obviously superior quality.
This is the Dumb Kid Syndrome: to overestimate one's skills despite being shown evidence to the contrary. This is a particularly difficult illusion to surmount as the individual or group isn't perceptive or smart enough to evaluate the contrary information properly. This syndrome applies to anyone who continues to maintain a theory, belief or self-perception despite being shown or experiencing copious amounts of evidence that contradicts their stance.
elegant simplicity
Elegant simplicity is a feature of good science. If explanations and/or equations are too messy or complicated, scientists continue to search for simplifications. Because of frequent validations over the centuries, it is believed that elegant simplicity is a feature of natural systems. Copernicus rejected Ptolemy's geocentric model of planetary motion because it lacked simplicity. For more on this topic check out Copernicus and Elegant Simplicity.
evo-emergence
Nearly everyone agrees that evolution occurs regularly on the micro-level. However there are big problems on the macro-level. This is the area most often attacked by those who don't believe in gradual evolution. How did the elements of the earth gradually evolve from matter to life, from no senses to the sense of smell, from one sex to two sexes, etcetera?
Some scientists have suggested that two complimentary processes are occurring instead of one. In addition to evolution, living systems also experience emergence. Emergence is when something has properties that are not contained in its component parts. Molecules generally have emergent properties that are not predictable from the atoms that make them up. This is why chemists are forever experimenting to discover new and useful features of unusual molecular compounds. The combination of two hydrogen and one oxygen atom does not predict the features of water.
According to this theory, the increasing complexity of matter yields emergent forms. Emergence has an unpredictable, almost divine, component that many scientists resist. To sidestep these thorny issues, we will refer to macro and microevolution together, as evo-emergence. It doesn't really matter whether pure evolution, mathematical emergence due to increasing complexity, or divine intervention leads to living evolution. The results are the same.
Experience
Experience has a precise technical meaning in the context of Information Dynamics theory. This definition coincides with, and yet is not identical with, the usual meaning of the word.
When the mental energy of conscious Attention focuses upon a data stream, the Living Algorithm begins to digest the incoming information. The Living Algorithm's digestion process transforms meaningless 1D instants into 2D moments. This transformation process is a step towards meaning.
When Attention is sustained upon the data stream for a sufficient length of time, the momentum of the 2D moments accumulates, until it produces a 3D Experience. According to the theory, this Experience produces memory traces via neural firings or some such process. In other words, an Experience is required to transfer and stabilize information into our memory banks.
This notion of Experience is at the foundation of the transfer of information energy into physical energy. When these Experiences accumulate in a similar fashion via sustained Attention, they eventually produce higher level Experiences that are at the heart of multi-dimensional mastery.
fungible
Fungible is a legal term that allows for an acceptable range of imprecision in the application of law. For instance, a baker is not found criminally liable if his loaf of bread is not exactly the same weight as advertised. The term recognizes that perfect accuracy of prediction is impractical, if not impossible. In this same sense, we suggest that fungible is a term that aptly applies to all living systems.
Living systems require a certain tolerance for imprecision (ambiguity) in both interpreting and responding to the constant flow of information. In order to recognize patterns, organisms must frequently overlook precise details in order to make rough (read practical) comparisons. ‘One can’t see the forest for the trees’ is a common metaphorical expression that recognizes how precise details can obscure patterns. It seems that living systems must have some mechanism whereby they can overlook extraneous details of sensory input to focus upon pattern. This mechanism gives precise details a fungible (approximate) meaning.
Consciousness requires the raw data of sensory input. However, this data is only useful if it has meaning. Some mechanism must digest the raw data for it to make sense to the organism. The digesting of information is an ongoing way of making sense of sensory experience.
The Living Algorithm's method of digesting information transforms the precise details of sensory data into ongoing rates of change/derivatives. These derivatives provide some rough (fungible) approximations as to the location, range and tendency of any flow of information. Even though these averages are just rough approximations, they provide the basis for the tentative working hypotheses that organisms require for survival.
Because we’re moving through time, these approximations are moving through time as well. Accordingly the Living Algorithm's derivatives create an ongoing relationship between data points. In creating this ongoing relationship, patterns are revealed. These patterns provide essential meaning to the organism. Due to the inherent imprecision of the process these patterns have a fungible characteristic that living systems require. (For clarification of these points check out the article: Living Algorithm's Fungible Meaning vs. Hard Science's Precision.)
The Rest Left to Avoid Tedious Linkage Changes
orthogonal
A mathematical term referring to perpendicular dimensions. These dimensions only intersect and interact along a single line - an infinitesimal amount of their entire surface area. Similarly physics and psychology interact to influence behavior within a limited zone. Otherwise they are independent of each other - with their own laws and principles. The notion of orthogonal planes is why it is unlikely that the science of physics will be able to precisely determine the behavior of living organism.
According to the theory, Information Dynamics is orthogonal to other disciplines. It is independent of the physical and psychological realms, while simultaneously interacting with them.
proto science
A logical system of thought that has no rigorous empirical evidence to back it up. It is waiting for testing to validate the theories. This is different from a pseudo science, which has been tested repeatedly with no conclusive results. Although there is an abundance of evidence supporting the theories of Information Dynamics, the scientific community has yet to perform rigorous experimentation to test its tenets. As such, it is still a proto science. After testing, it becomes either a pseudo or a real science.
pseudo science
A logical system of thought that has no rigorous empirical evidence to back it up. As contrasted with a proto science, the scientific community has performed numerous experiments that have failed to support its tenets.
For instance, astrology is based upon an elaborate system of correspondences between time of birth, personality, planetary interactions, and earthly events. Although an uncountable number of books have been written over millennia regarding these connections, it is not considered a science because no experiments executed with repeatable scientific rigor have verified the validity of any of these correspondences. Although this does not disprove astrology, the inconclusive results leave it in the realm of a pseudo science.
Similarly until Newton's laws were verified through observation his was but a pseudo science. This holds true for Information Dynamics as well. Until repeatable experiments can be performed which validate specific theories, the logical structure of correspondences remains a proto or pseudo science.
sustained attention
The ability of complex forms of life to focus consciousness upon a certain topic of interest for an extended length of time. A predator focusing consciousness upon prey to obtain food – the male focusing upon the female of the species for reproductive purposes – the artist focusing upon a painting to produce beauty - or even a mob focusing upon a perceived injustice to wreak revenge – are all examples of this type.
According to Lehman’s Theory of Attention, the Pulse from Data Stream Dynamics reveals the mechanisms behind Sustained Attention. According to the theory, a Pulse of Sustained Attention is required to generate an Experience. Experience lies at the heart of information transfer into the physical structure of the neural networks to generate and stabilize a memory.
syllogism
"the logical form of an argument consisting of three statements, two premises and a conclusion. The conclusion of a valid syllogism follows logically from the premises and is true if the premises are true." (Desk Encyclopedia)
In the classic writings of Aristotle and his followers, the syllogism was more specifically defined as being of 3 types: categorical, hypothetical, and disjunctive. However Aristotle gave this meta-definition of a syllogism. "A syllogism is a discourse in which, certain things being posited, something else follows from them by necessity." This is the essence of deductive reasoning. Although we will attempt to stick to the two premise form, sometimes we will use the word syllogism to refer to a deductive argument of any length.